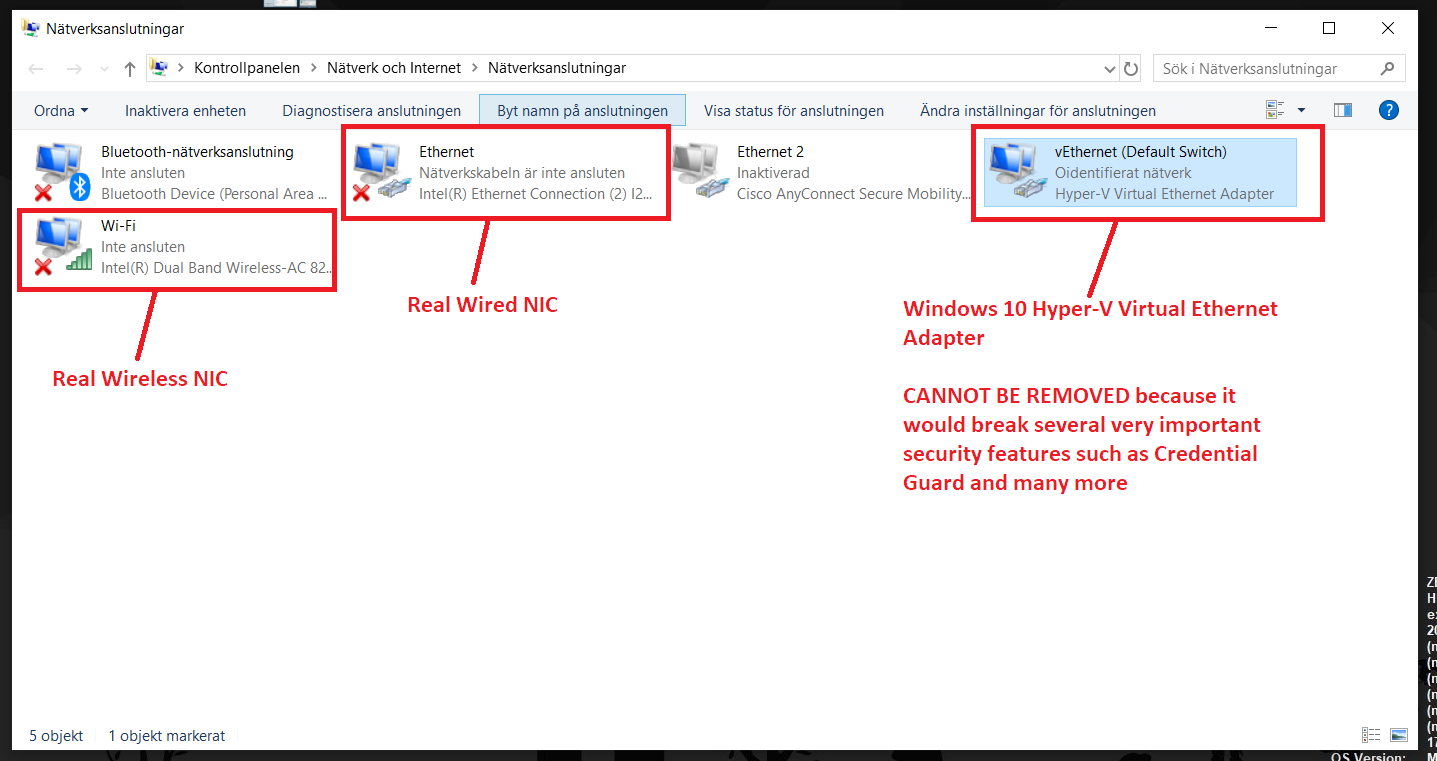
Objective
Both are using NAT/Shared network configuration. I then did an ipconfig /all on both VMs to compare. On both VMs, the 'Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client Virtual Miniport Adapter for Windows x64' shows up, and are basically identical aside from IPV6 address, and IPv4 Address are one digit apart, obviously not the same. AnyConnect - Showing no internet access when connected, however you can route to the internet? Windows tries to download a file from Microsoft to verify network access. Buy 2 Catalyst 9300 48-port multigigabit switches with a Cisco DNA Advantage or Premier license, and get 4 Catalyst 9130 Access Points free. And while there are new routing entries for the Cisco VPN adapter, no existing routing entries were modified after connection: It is to be expected that we cannot ping Speeder’s IP address on the Cisco VPN adapter (192.168.199.20) because it is on a different subnet than our network (we are 10.0.x.x 255.255.0.0), i.e.
The objective of this document is to show you basic troubleshooting steps on some common errors on the Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client. When installing the Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client, errors may occur and troubleshooting may be needed for a successful setup.
Note that the errors discussed in this document is not an exhaustive list and varies with the configuration of the device used.
For additional information on AnyConnect licensing on the RV340 series routers, check out the article AnyConnect Licensing for the RV340 Series Routers.
Software Version
AnyConnect v4.x (Link to download)
Basic Troubleshooting on Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client Errors
Note: Before attempting to troubleshoot, it is recommended to gather some important information first about your system that might be needed during the troubleshooting process. To learn how, click here.
1. Problem: Network Access Manager fails to recognize your wired adapter.
Solution: Try unplugging your network cable and reinserting it. If this does not work, you may have a link issue. The Network Access Manager may not be able to determine the correct link state of your adapter. Check the Connection Properties of your Network Interface Card (NIC) driver. You may have a 'Wait for Link' option in the Advanced Panel. When the setting is On, the wired NIC driver initialization code waits for auto negotiation to complete and then determines if a link is present.
2. Problem: When AnyConnect attempts to establish a connection, it authenticates successfully and builds the Secure Socket Layer (SSL)session, but then the AnyConnect client crashes in the vpndownloader if using Label-Switched Path (LSP) or NOD32 Antivirus.
Solution: Remove the Internet Monitor component in version 2.7 and upgrade to version 3.0 of ESET NOD32 AV.
3. Problem: If you are using an AT&T Dialer, the client operating system sometimes experiences a blue screen, which causes the creation of a mini dump file.
Solution: Upgrade to the latest 7.6.2 AT&T Global Network Client.
4. Problem: When using McAfee Firewall 5, a User Datagram Protocol (UDP)Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) connection cannot be established.
Solution: In the McAfee Firewall central console, choose Advanced Tasks > Advanced options and Logging and uncheck the Block incoming fragments automatically check box in McAfee Firewall.
5. Problem: The connection fails due to lack of credentials.
Solution: The third-party load balancer has no insight into the load on the Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) devices. Because the load balance functionality in the ASA is intelligent enough to evenly distribute the VPN load across the devices, using the internal ASA load balancing instead is recommended.
6. Problem: The AnyConnect client fails to download and produces the following error message:
Solution: Upload the patch update to version 1.2.1.38 to resolve all dll issues.
7. Problem: If you are using Bonjour Printing Services, the AnyConnect event logs indicate a failure to identify the IP forwarding table.
Solution: Disable the Bonjour Printing Service by typing net stop “bonjour service” at the command prompt. A new version of mDNSResponder (1.0.5.11) has been produced by Apple. To resolve this issue, a new version of Bonjour is bundled with iTunes and made available as a separate download from the Apple web site.
8. Problem: An error indicates that the version of TUN or network tunnel is already installed on this system and is incompatible with the AnyConnect client.
Solution: Uninstall the Viscosity OpenVPN Client.
9. Problem: If a Label-Switched Path (LSP) module is present on the client, a Winsock catalog conflict may occur.
Solution: Uninstall the LSP module.
10. Problem: If you are connecting with a Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) router, DTLS traffic may fail even if successfully negotiated.
Solution: Connect to a Linksys router with factory settings. This setting allows a stable DTLS session and no interruption in pings. Add a rule to allow DTLS return traffic.
11. Problem: When using AnyConnect on some Virtual Machine Network Service devices, performance issues have resulted.
Solution: Uncheck the binding for all IM devices within the AnyConnect virtual adapter. The application dsagent.exe resides in C:WindowsSystemdgagent. Although it does not appear in the process list, you can see it by opening sockets with TCPview (sysinternals). When you terminate this process, normal operation of AnyConnect returns.
12. Problem: You receive an “Unable to Proceed, Cannot Connect to the VPN Service” message. The VPN service for AnyConnect is not running.
Solution: Determine if another application conflicted with the service by going to the Windows Administration Tools then make sure that the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Agent is not running. If it is running and the error message still appears, another VPN application on the workstation may need to be disabled or even uninstalled. After taking that action, reboot, and repeat this step.
13. Problem: When Kaspersky 6.0.3 is installed (even if disabled), AnyConnect connections to the ASA fail right after CSTP state = CONNECTED. The following message appears:
Solution: Uninstall Kaspersky and refer to their forums for additional updates.
14. Problem: If you are using Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS), the following termination error is returned to the event log when AnyConnect attempts to establish a connection to the host device:
Solution: Disable the RRAS service.
15. Problem: If you are using a EVDO wireless card and Venturi driver while a client disconnect occurred, the event log reports the following:
Solutions:
- Check the Application, System, and AnyConnect event logs for a relating disconnect event and determine if a NIC card reset was applied at the same time.
- Ensure that the Venturi driver is up to date. Disable Use Rules Engine in the 6.7 version of the AT&T Communications Manager.
If you encounter other errors, contact the support center for your device.
For further information and community discussion on AnyConnect licensing updates, click here.
For AnyConnect Licensing FAQs, click here.
Introduction
This document describes how to troubleshoot some of the most common communication issues of the Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client on Firepower Threat Defense (FTD) when it uses either Secure Socket Layer (SSL) or Internet Key Exchange version 2 (IKEv2).
Contributed by Angel Ortiz and Fernando Jimenez, Cisco TAC Engineers.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:

- Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client.
- Cisco FTD.
- Cisco Firepower Management Center (FMC).
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
- FTD managed by FMC 6.4.0.
- AnyConnect 4.8.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Recommended troubleshoot process
This guide explains how to troubleshoot some common communication issues that AnyConnect clients have when the FTD is used as Remote Access Virtual Private Network (VPN) gateway. These sections address and provide solutions to problems below:
- AnyConnect clients cannot access internal resources.
- AnyConnect clients do not have internet access.
- AnyConnect clients cannot communicate between each other.
- AnyConnect clients cannot establish phone calls.
- AnyConnect clients can establish phone calls. However, there is no audio on the calls.
AnyConnect clients cannot access internal resources
Complete these steps:
Step 1. Verify Split tunnel configuration.
- Navigate to the Connection Profile that AnyConnect clients are connected to: Devices > VPN > Remote Access > Connection Profile > Select the Profile.
- Navigate to the Group-Policy assigned to that Profile: Edit Group Policy > General.
- Check the Split Tunneling configuration, as shown in the image.
- If it's configured as Tunnel networks specified below, verify the Access Control List (ACL) configuration:
Navigate to Objects > Object Management > Access List > Edit the Access List for Split tunneling.
- Ensure that the networks that you try to reach from the AnyConnect VPN client are listed in that Access List, as shown in the image.
Step 2.Verify Network Address Translation (NAT) exemption configuration.
Remember that we must configure a NAT exemption rule to avoid traffic to be translated to the interface IP address, usually configured for internet access (with Port Address Translation (PAT)).
- Navigate to the NAT configuration: Devices > NAT.
- Ensure that the NAT exemption rule is configured for the correct source (internal) and destination (AnyConnect VPN Pool) networks. Also check that the correct source and destination interfaces have been selected, as shown in the image.
Note: When NAT exemption rules are configured, check the no-proxy-arp and perform route-lookup options as a best practice.
Step 3. Verify Access Control Policy.
Per your Access Control Policy configuration, ensure that traffic from the AnyConnect clients is allowed to reach the selected internal networks, as shown in the image.
AnyConnect clients do not have internet access
There are two possible scenarios for this issue.
- Traffic destined for the internet must not go through the VPN tunnel.
Ensure that the Group-Policy is configured for Split tunneling as Tunnel networks specifiedbelow and NOT as Allow all traffic over tunnel, as shown in the image.
2. Traffic destined for the Internet must go through the VPN tunnel.
In this case, the most common Group-Policy configuration for Split tunneling would be to select Allow all traffic over tunnel, as shown in the image.
Step 1. Verify NAT exemption configuration for internal network reachability.
Remember that we must still configure a NAT exemption rule to have access to the internal network. Please review Step 2 of the AnyConnect clients cannot access internal resource section.

Step 2. Verify hairpinning configuration for dynamic translations.
In order for AnyConnect clients to have internet access through the VPN tunnel, we need to ensure that the hairpinning NAT configuration is correct for traffic to be translated to the interface´s IP address.
- Navigate to the NAT configuration: Devices > NAT.
- Ensure that the Dynamic NAT rule is configured for the correct interface (Internet Service Provider (ISP) link) as source and destination (hairpinning). Also check that the network used for the AnyConnect VPN address pool is selected in Original source and the Destination Interface IP option is selected for Translated source, as shown in the image.
Step 3. Verify Access Control Policy.
Per your Access Control Policy configuration, ensure that traffic from the AnyConnect clients is allowed to reach the external resources, as shown in the image.
AnyConnect clients cannot communicate between each other
There are two possible scenarios for this issue:
- AnyConnect clients with Allow all traffic over tunnel configuration in place.
- AnyConnect clients with Tunnel networks specified below configuration in place.
- AnyConnect clients with Allow all traffic over tunnel configuration in place.
When Allow all traffic over tunnel is configured for AnyConnect means that all traffic, internal and external, should be forwarded to the AnyConnect headend, this becomes a problem when you have NAT for Public Internet access, since traffic comes from an AnyConnect client destined to another AnyConnect client is translated to the interface IP address and therefore communication fails.
Step 1. Verify NAT exemption configuration.
In order to overcome this problem a manual NAT exemption rule must be configured to allow bidirectional communication within the AnyConnect clients.
- Navigate to the NAT configuration: Devices > NAT.
- Ensure that the NAT exemption rule is configured for the correct source (AnyConnect VPN Pool) and destination. (AnyConnect VPN Pool) networks. Also check that the correct hairpin configuration is in place, as shown in the image.
Step 2. Verify Access Control Policy.
Per your Access Control Policy configuration, ensure that traffic from the AnyConnect Clients is allowed, as shown in the image.
2. Anyconnect clients with Tunnel networks specified below configuration in place.
With Tunnel networks specified below configured for the AnyConnect clients only specific traffic is forwarded to through the VPN tunnel. However, we need to ensure that the headend has the proper configuration to allow communication within the AnyConnect clients.
Step 1. Verify NAT exemption configuration.
Please check Step 1, in the Allow all traffic over tunnel section.
Step 2. Verify Split tunneling configuration.
For AnyConnect clients to communicate between them we need to add the VPN pool addresses into the Split-Tunnel ACL.
- Please follow Step 1 of the AnyConnect clients cannot access internal resources section.
- Ensure that the AnyConnect VPN Pool network is listed in the Split tunneling Access List, as shown in the image.
Note: If there is more than one IP Pool for AnyConnect clients and communication between the different pools is needed, ensure to add all of the pools in the split tunneling ACL, also add a NAT exemption rule for the needed IP Pools.
Step 3. Verify Access Control Policy.
Ensure that traffic from the AnyConnect clients is allowed as shown in the image.
AnyConnect clients cannot establish phone calls
There are some scenarios where AnyConnect clients need to establish phone calls and video conferences over VPN.
AnyConnect clients can connect to the AnyConnect headend without any problem. They can reach internal and external resources, however phone calls cannot be established.
For this cases we need to consider the follow points:
- Network topology for voice.
- Protocols involved. I.e. Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP), etc.
- How the VPN phones connect to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CUCM).
By default, FTD and ASA have applications inspection enabled by default in their global policy-map.
In most cases scenarios the VPN phones are not able to establish a reliable communication with the CUCM because the AnyConnect headend has an application inspection enabled that modifies the signal and voice traffic.
For more information about the voice and video application where you can apply application inspection see the follow document:
In order to confirm if an application traffic is dropped or modified by the global policy-map we can use the show service-policy command as shown below.
In this case we can see how SIP inspection drops the traffic.
Moreover, SIP inspection can also translate IP addresses inside the payload, not in the IP header, causes different issues, hence it is recommended to disable it when we want to use voice services over AnyConnect VPN.
In order to disable it we need to complete the next steps:
Step 1. Enter the privileged EXEC mode.
For more information on how to access this mode see the next document:
Step 2. Verify the global policy-map.
Run the next command and verify if SIP inspection is enabled.
Step 3. Disable SIP inspection.
If SIP inspection is enabled, turn it off running command below from clish prompt:
Bollywood punjabi movies all softwares. Step 4. Verify the Global Policy-map again.
Ensure that SIP inspection is disabled from the global policy-map:
AnyConnect clients can establish phone calls, however there is no audio on the calls
As mentioned in the previous section, a very common need for AnyConnect clients is to establish phone calls when connected to the VPN. In some cases the call can be established, however clients may experience lack of audio on it. This applies to the next scenarios:
- No audio on the call between an AnyConnect client and an external number.
- No audio on the call between an AnyConnect client and another AnyConnect client.
In order to get this fixed, we can follow these steps:
Step 1. Verify Split tunneling configuration.

- Navigate to the Connection Profile use to connect to: Devices > VPN > Remote Access > Connection Profile > Select the Profile.
- Navigate to the Group-Policy assigned to that Profile: Edit Group Policy > General.
- Check the Split Tunneling configuration, as shown in the image.
- If configured as Tunnel networks specified below, verify the Access List configuration: Objects > Object Management > Access List > Edit the Access List for Split tunneling.
- Ensure that the Voice Servers and the AnyConnect IP Pool networks are listed in the Split tunneling Access List, as shown in the image.
Step 2. Verify NAT exemption configuration.
NAT exemption rules must be configured to exempt traffic from the AnyConnect VPN network to the Voice Servers network and also to allow bidirectional communication within the AnyConnect clients.
- Navigate to the NAT configuration: Devices > NAT.
- ensure that the NAT exemption rule is configured for the correct source (Voice Servers) and destination (AnyConnect VPN Pool) networks, and the hairpin NAT rule to allow AnyConnect client to AnyConnect client communication is in place. Moreover, check that the correct inbound and outbound interfaces configuration is in place for each rule, per your network design, as shown in the image.
Cisco Anyconnect No Network Adapters
Step 3. Verify that SIP inspection is disabled.
Please review the previous section AnyConnect clients cannot establish phone calls to know how to disable SIP inspection.
Cisco Anyconnect Network Repair
Step 4. Verify Access Control Policy.
Per your Access Control Policy configuration, ensure that traffic from the AnyConnect clients is allowed to reach the Voice servers and involved networks, as shown in the image.
Related Information
- This video provides the configuration example for the different issues discussed in this document.
- For additional assistance, please contact Technical Assistance center (TAC). A valid support contract is required: Cisco Worldwide Support Contacts.
Ipv4 No Network Access
- You can also visit the Cisco VPN Community here.
